Choosing between a magnetic drive pump and a peristaltic pump largely comes down to the fluid you are wanting to pump and the type of application. Magnetic drive pumps us e magnets to turn the drive shaft while peristaltic pumps use the compression of a tube or hose to create suction.
Let’s take a look at exactly how these two pumps differ and what their unique advantages and disadvantages are.
How does a magnetic drive pump work?
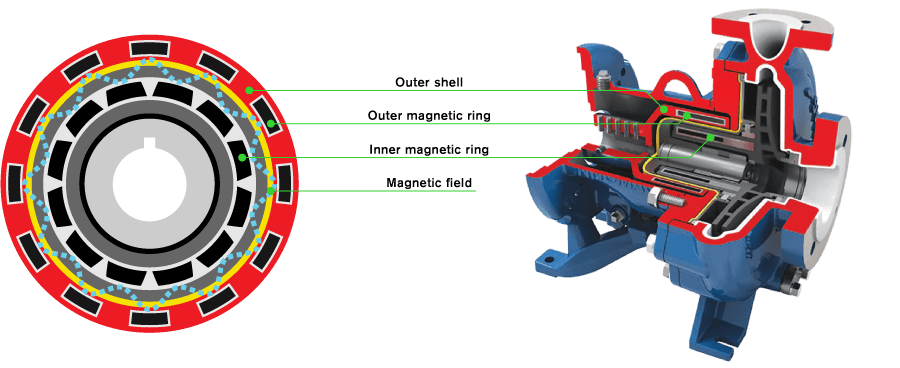
Magnetic drive pumps work differently from most other pumps. They are a type of centrifugal pump but instead of a shaft being connected from the motor to the impeller, they use magnets to rotate the impeller. Because magnetism is used, there is no need for actual physical contact between the drive shaft and the impeller. A hermetically sealed area therefore prevents fluids from leaving the pump.
This frictionless design has a number of advantages, which we’ll discuss down below, but it’s greatest asset is being able to move corrosive liquids without any leakage.
Advantages of magnetic pumps
- low maintenance, lasts years without needing anything replaced
- low leak risk, retains all vapors inside the system making it a good option for hazardous fluids
- extremely reliable
- coupling is easy as it is not necessary to align the pump and motor like in other pump designs
Disadvantages of magnetic pumps
- cannot run dry
- doesn’t handle fluids containing large solid content
How does a peristaltic hose pump work?
Peristaltic pumps work using a principle known as peristalsis. This term comes from biology and refers to the way our muscles contract and relax to move fluids around our digestive tract.
In essence, peristaltic pumps work, not by creating pressure differences through an impeller or drive shaft, but through the contraction and expansion of a tube or hose.
The tube or hose is compressed in places through a series of rollers or pressing shoes that rotate. When the rollers press into the tube, they push fluid and any air out of that segment of the tube or hose. This creates a vacuum. When the rollers pull away from the tube and it relaxes, the vacuum sucks new fluid into that section.
This process is repeated over and over to push and pull fluid, transporting it to its destination.

Advantages of peristaltic pumps
- no valves, glands, or seals to replace
- most maintenance only requires replacement of the tube or hose
- gentle pumping suited for shear sensitive materials
- handle corrosive materials well
- self-priming and can dry run
- flow can be reversed to clean lines or blockages
- accurate dosing for sensitive materials
Disadvantages of peristaltic pumps
- pulsing flow that isn’t suitable for applications where consistent flow rate is required
- relatively high power usage due to the drive motor continually squeezing the tube
If you need any help selecting a magnetic drive or peristaltic hose pump for your tough pumping challenge, contact one of our experts today.

